* Split libraries and wasm devcontainers Codespaces allows for monorepo support now. So we can have different pre-builds for different dev environments. Creating a "libraries" pre-build and a "wasm" pre-build devcontainer. * Move devcontainer files into separate folders * Path up a directory to the Dockerfile * Split the Dockerfile so it can be customized per devcontainer * Update Codespaces docs * Respond to PR feedback * Use the new open devcontainers path. * Use the GH CLI feature instead of installing it ourselves * Set hostRequirements for Codespaces Developing in dotnet/runtime with a 2-core / 4GB ram machine doesn't work very well. Add a minimum of 4-core machine to the devcontainer spec. Fix #75680
3.3 KiB
Using Codespaces
Codespaces allows you to develop in a Docker container running in the cloud. You can use an in-browser version of VS Code or the full VS Code application with the GitHub Codespaces VS Code Extension. This means you don't need to install dotnet/runtime's prerequisites on your current machine in order to develop in dotnet/runtime.
Create a Codespace
dotnet/runtime runs a nightly GitHub Action to build the latest code in the repo. This allows you to immediately start developing and testing after creating a codespace without having to build the whole repo. When the machine is created, it will have built the repo using the code as of 6 AM UTC that morning.
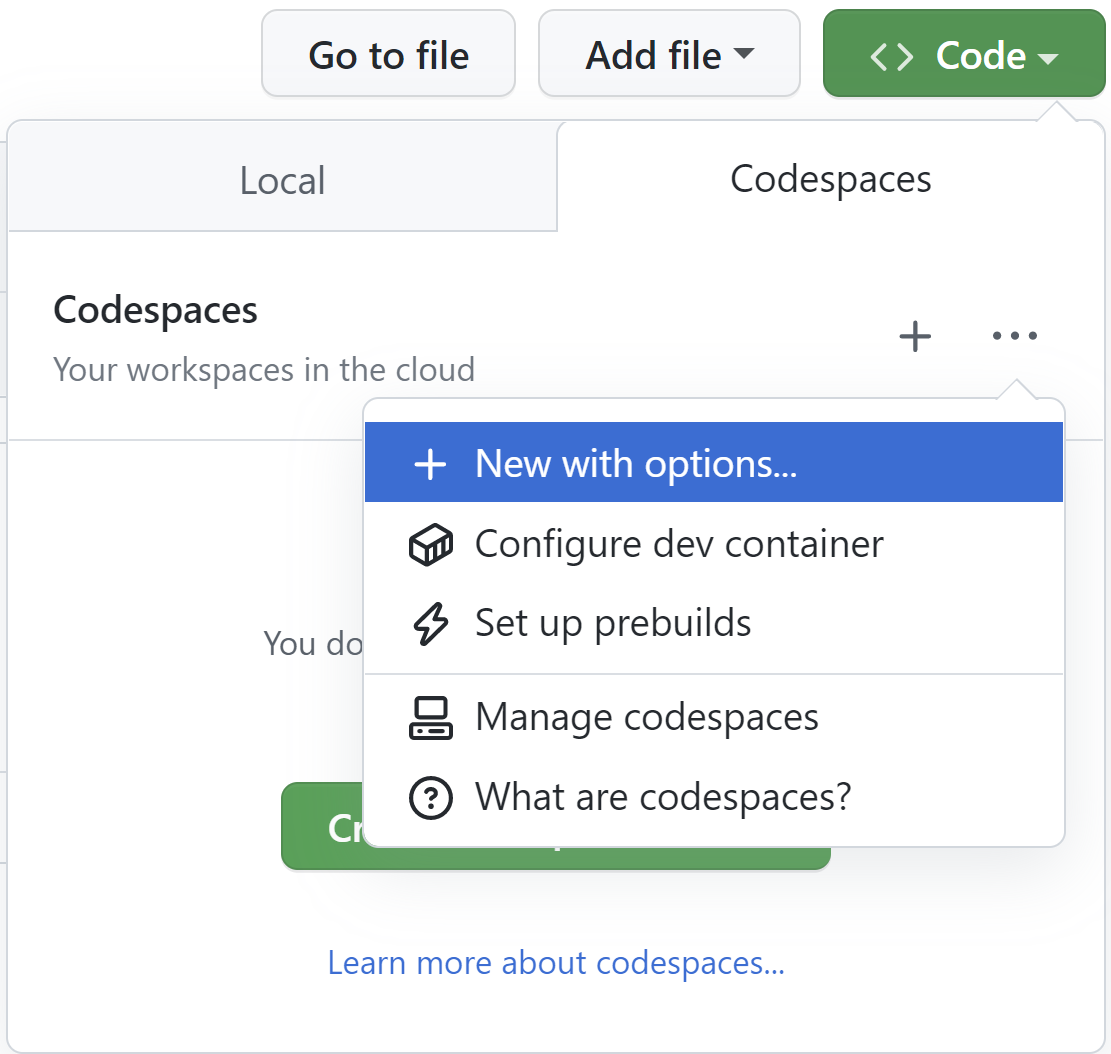
- From https://github.com/dotnet/runtime, drop-down the
Codebutton and select theCodespacestab.
- Click the drop-down at the side of the
Create codespace on mainbutton and selectConfigure and create codespace
- Select which Dev container configuration you want to use.
- For `libraries` work, pick `.devcontainer/libraries/devcontainer.json`.
- For `WASM` work, pick `.devcontainer/wasm/devcontainer.json`.
- Select the Machine type. For
dotnet/runtime, it is recommended to select at least a4-coremachine. You can also verify that aPrebuildis ready.
If these instructions are out of date, see https://docs.github.com/codespaces/developing-in-codespaces/creating-a-codespace#creating-a-codespace for instructions on how to create a new codespace.
Updating dotnet/runtime's Codespaces Configuration
The Codespaces configuration is spread across the following places:
- The .devcontainer folder contains folders for each "development scenario":
libraries- Used by developers working insrc/librarieswasm- Used by developers working on the browser-wasm workload- The
scriptsfolder contains any scripts that are executed during the creation of the codespace. This has the build command that builds the entire repo for prebuilds.
- Each development scenario folder contains:
devcontainer.jsonfile configures the codespace and has VS Code / Environment settings- The Dockerfile used to create the Docker image
- The GitHub Action can be configured by following the instructions at https://docs.github.com/codespaces/prebuilding-your-codespaces/configuring-prebuilds.
To test out changes to the .devcontainer files, you can follow the process in Applying changes to your configuration docs. This allows you to rebuild the Codespace privately before creating a PR.
To test out your changes you can run the Codespaces Prebuilds Action in your fork against a branch with your changes.