mirror of
https://github.com/VSadov/Satori.git
synced 2025-06-10 01:50:53 +09:00
Split Codespaces configuration based on development scenarios (#74683)
* Split libraries and wasm devcontainers Codespaces allows for monorepo support now. So we can have different pre-builds for different dev environments. Creating a "libraries" pre-build and a "wasm" pre-build devcontainer. * Move devcontainer files into separate folders * Path up a directory to the Dockerfile * Split the Dockerfile so it can be customized per devcontainer * Update Codespaces docs * Respond to PR feedback * Use the new open devcontainers path. * Use the GH CLI feature instead of installing it ourselves * Set hostRequirements for Codespaces Developing in dotnet/runtime with a 2-core / 4GB ram machine doesn't work very well. Add a minimum of 4-core machine to the devcontainer spec. Fix #75680
This commit is contained in:
parent
bff967bdd3
commit
55060ebf68
7 changed files with 177 additions and 57 deletions
|
|
@ -7,9 +7,20 @@ dotnet/runtime runs a nightly GitHub Action to build the latest code in the repo
|
|||
|
||||
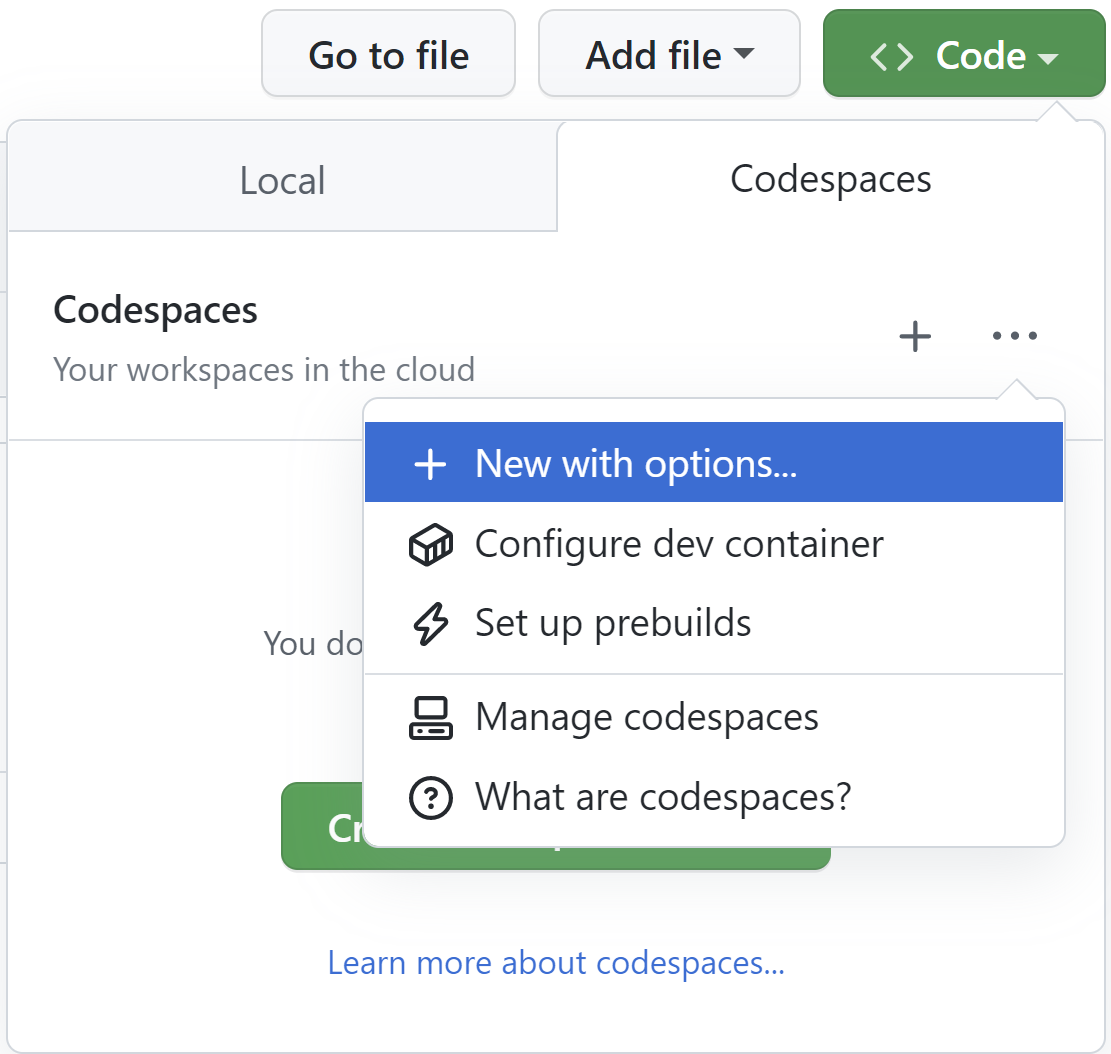
1. From https://github.com/dotnet/runtime, drop-down the `Code` button and select the `Codespaces` tab.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. Select the Machine type. For dotnet/runtime, it is recommended to select at least a `4-core` machine. You can also verify that a "Prebuild" is ready.
|
||||
2. Click the drop-down at the side of the `Create codespace on main` button and select `Configure and create codespace`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. Select which Dev container configuration you want to use.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- For `libraries` work, pick `.devcontainer/libraries/devcontainer.json`.
|
||||
- For `WASM` work, pick `.devcontainer/wasm/devcontainer.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Select the Machine type. For `dotnet/runtime`, it is recommended to select at least a `4-core` machine. You can also verify that a `Prebuild` is ready.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,21 +31,15 @@ dotnet/runtime runs a nightly GitHub Action to build the latest code in the repo
|
|||
|
||||
The Codespaces configuration is spread across the following places:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The [.devcontainer](../../.devcontainer) folder contains:
|
||||
- `devcontainer.json` file configures the codespace and mostly has VS Code settings
|
||||
- The Dockerfile used to create the image
|
||||
1. The [.devcontainer](../../.devcontainer) folder contains folders for each "development scenario":
|
||||
- `libraries` - Used by developers working in `src/libraries`
|
||||
- `wasm` - Used by developers working on the browser-wasm workload
|
||||
- The `scripts` folder contains any scripts that are executed during the creation of the codespace. This has the build command that builds the entire repo for prebuilds.
|
||||
2. The GitHub Action can be configured by following the instructions at https://docs.github.com/codespaces/prebuilding-your-codespaces/configuring-prebuilds.
|
||||
2. Each development scenario folder contains:
|
||||
- `devcontainer.json` file configures the codespace and has VS Code / Environment settings
|
||||
- The Dockerfile used to create the Docker image
|
||||
3. The GitHub Action can be configured by following the instructions at https://docs.github.com/codespaces/prebuilding-your-codespaces/configuring-prebuilds.
|
||||
|
||||
To test out changes to the `.devcontainer` files, you can follow the process in [Applying changes to your configuration](https://docs.github.com/codespaces/customizing-your-codespace/configuring-codespaces-for-your-project#applying-changes-to-your-configuration) docs. This allows you to rebuild the Codespace privately before creating a PR.
|
||||
|
||||
To test out your `.yml` changes, here is the process:
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: *Executing these steps will overwrite the current prebuilt container for the entire repo. Afterwards, anyone creating a new codespace will get a prebuilt machine with your test changes until the Action in `main` is executed again.*
|
||||
|
||||
1. Edit and commit the files to a branch.
|
||||
2. Push that to a branch on dotnet/runtime. Be careful that you aren't pushing to `main` or some other important branch. Prefix your branch name with your GitHub account name, so others know it is a dev branch. ex. `username/FixCodespaces`.
|
||||
3. In the "Actions" tab at the top of dotnet/runtime:
|
||||
- Select "Create Codespaces Prebuild" action on the left
|
||||
- On the right click "Run workflow" and pick your branch
|
||||
- After it runs, try to create a codespace
|
||||
To test out your changes you can run the [Codespaces Prebuilds Action](https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/actions/workflows/codespaces/create_codespaces_prebuilds) in your fork against a branch with your changes.
|
||||
BIN
docs/workflow/codespace-dev-container-configuration.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/workflow/codespace-dev-container-configuration.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB |
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue